Inflation, what a disaster. Interest rates were raised by a quarter point (0.25%) today, 25 basis points. The FOMC, Federal Open Market Committee, meets 8 times a year to discuss the ongoing economic environment. This is the FED’s first interest rate hike since December 2018, and the long term outlook is full of more rate hikes.
Federal Reserve Chairman Jerome Powell made it clear that their focus on controlling, or taming, inflation can come with “quicker action” if it is necessary. Showing that rate hikes are not only limited to their scheduled meetings.
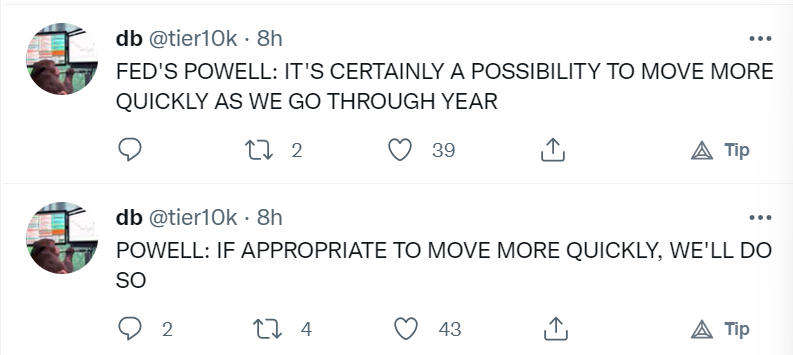
Everyone’s question is if they will hold off, or maintain their expectations. After the last few years of “kicking the can” nobody is sure of what to expect.
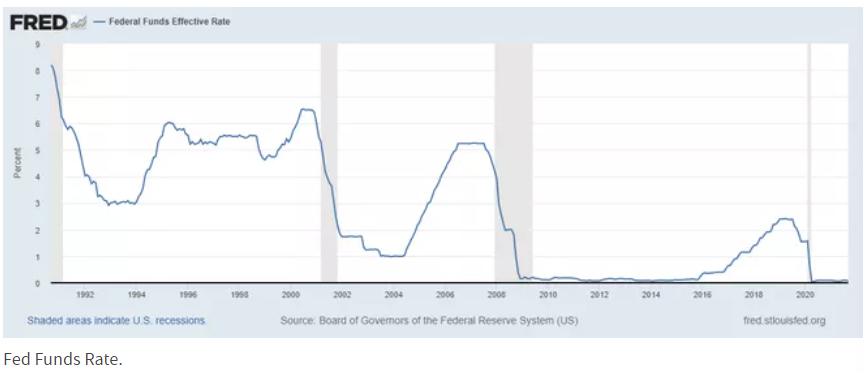
The Federal Funds Rate
Today’s rate hike will bring the new range of the federal funds rate to 0.25% – 0.5%. The Federal Funds rate is important for a number of reasons aside from the effect that it has on the stock market. The FED previously lowered the federal funds rate to 0% – 0.25% 2 years ago in a response to the COVID outbreak.
This rate will effect consumers directly as the short term implications include short-term interest rates on things like home and auto loans, and of course credit cards. Over the long term you can see the federal fund’s rate below.
The next FOMC meeting is May 3 – 4 and the plan is for another rate hike as they attempt to suppress and control the “sudden spike in inflation” that they “did not expect”.
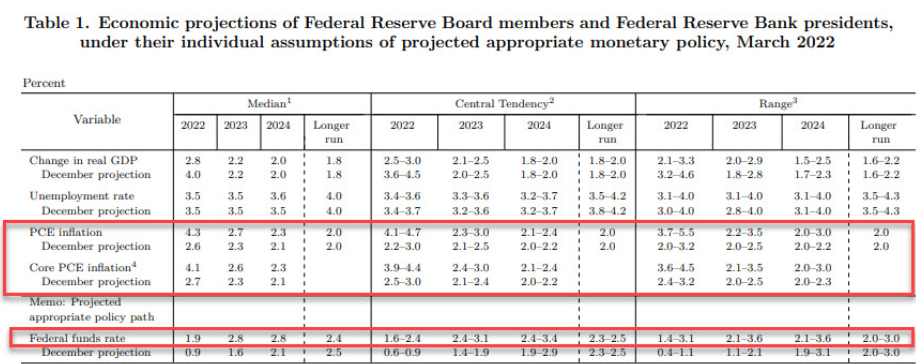
Their outlook is still to target the 2% inflation objective and for the unemployment numbers to continue to decline amidst a strong labor market. Their strong projection of 6 rate hikes would put the funds rate right under their 2% target.
The FED Balance Sheet
The FOMC is expecting in the coming months, stated as targeting the second half of the year for reducing the FED balance sheet. This is reducing the holdings of US Treasuries, and mortgage backed securities (MBS) amounting now to ~ $9T.
“In addition, the Committee expects to begin reducing its holdings of Treasury securities and agency debt and agency mortgage-backed securities at a coming meeting.”
FOMC
Jerome Powell stated that these reductions in the Federal balance should be expected to occur around May.
“Indicators of economic activity and employment have continued to strengthen. Job gains have been strong in recent months, and the unemployment rate has declined substantially. Inflation remains elevated, reflecting supply and demand imbalances related to the pandemic, higher energy prices, and broader price pressures.”
Federal Reserve FOMC Statement
The situation over in Ukraine is adding to the uncertainty in the economy in the near term. Certainly leading people to see that this will also add to the ongoing inflationary pressures we are seeing. Don’t expect it to subside anytime soon.
It is obvious the narrative is blaming the inflationary crisis all on Putin and using him as the scapegoat they desperately need.
Treasury Secretary Janet Yellen stated earlier this week, “Americans will likely see another year of ‘very uncomfortably high’ inflation”. Contradicting Powell’s words today on inflation.
There is no debate that the inflationary situation isn’t goin away any time soon, and things are likely going to get worse before they get better. The “CPI” is 8% and the PPI (Producer Price Index) is 10%. The PPI is different from the CPI as it is measuring the cost to make products.
We’re currently in an inflationary crisis, and people are struggling to navigate the situation. Supply chain “bottlenecks”, and economic sanctions are changing international trade and even have Russia and Saudi Arabia considering big changes and are discussing moving toward the Yuan in a big way. This will be something to keep track of over the short term.
Economic growth expectations have also been slashed for the rest of the year. Expectations were set at 4.0% GDP at the start of the year, and have been cut down to 2.8%. A complete reversal.
Summary
The FED approved an increase to interest rates for the first time in 3 years. A small change that is looking to be the first of many interest rate hikes. Jerome Powell and the FED are tasked with maintaining low unemployment (currently at 3.8%) and decreasing the FED balance sheet of US Treasuries and MBS.
There are 6 more meetings ahead, with next one scheduled May 3 & 4. Chances are another rate hike of 25 bps.